TECHNOLOGY
Maximizing Efficiency with SSIS-950: Best Practices for Developers

Data integration is a cornerstone of modern analytics, and SSIS-950 stands out as a powerful tool in this realm. For developers looking to streamline their workflows, reduce complexity, and ensure robust data handling, mastering SSIS-950 can be transformative. This version offers enhanced features that not only simplify the development process but also optimize performance for large-scale projects. Whether you’re just starting with SQL Server Integration Services or looking to deepen your expertise, there’s much to explore in leveraging SSIS-950 effectively. Let’s dive into the benefits it brings and discover best practices that can elevate your projects from ordinary to extraordinary!
Understanding the Benefits of SSIS-950 for Developers
SSIS-950 offers a range of benefits that can significantly enhance a developer’s workflow. One of the key advantages is its streamlined data integration capabilities. Developers can efficiently consolidate data from multiple sources, simplifying workflows and reducing manual intervention.
Another notable benefit is improved performance tuning. The SSIS-950 framework provides built-in tools for monitoring and analyzing package execution, allowing developers to identify bottlenecks quickly. This insight leads to faster processing times and more efficient resource usage.
Additionally, SSIS-950 promotes better collaboration among teams. With enhanced version control features, multiple developers can work on projects simultaneously without conflicts. This fosters an environment where innovation thrives while maintaining project integrity.
The user-friendly interface also makes it easier for new team members to get up to speed. Quick onboarding reduces downtime and enhances overall productivity within development teams.
Best Practices for Designing and Building SSIS Packages
When designing and building SSIS packages, clarity is key. Start by defining clear objectives for each package. This will guide your design and ensure that every component serves a purpose.
Keep the architecture simple. Avoid unnecessary complexity to enhance maintainability. A straightforward structure helps team members understand the workflow with ease.
Modular design can be beneficial too. Break down tasks into smaller, reusable components or packages. This approach not only streamlines development but also improves debugging efficiency.
Document everything comprehensively as you go along. Capture essential details about data sources, transformations, and workflows in your documentation to facilitate future updates.
Always test rigorously before deployment. Thorough testing ensures that any errors are identified early on and enhances overall stability in production environments.
Tips for Optimizing Performance in SSIS-950
To optimize performance in SSIS-950, start with efficient data flow design. Use the right transformations and minimize unnecessary steps. Keep your data sources lean by selecting only the columns you need.
Parallel processing is another powerful feature in SSIS-950. Leverage it to execute tasks simultaneously, reducing overall execution time. Monitor thread counts carefully to avoid overwhelming your system resources.
Connection managers should be configured for optimal use as well. Ensure that they are re-used where possible, which can significantly cut down on connection overhead.
Additionally, consider using fast load options when inserting large datasets into SQL Server destinations. This method enhances speed while minimizing logging impacts.
Always test package execution under various loads and scenarios before deploying them in production environments. Regularly revisiting these practices will help maintain peak performance over time.
Managing and Maintaining SSIS Projects with Version Control
Implementing version control in SSIS projects is crucial for maintaining the integrity of your data workflows. It allows developers to track changes, collaborate effectively, and revert back to previous versions when needed.
Using tools like Git or Azure DevOps can streamline this process. You can create repositories that encompass all components of your SSIS packages, ensuring easy access for team members.
Establish a consistent naming convention for commits and branches. This practice enhances clarity and helps identify specific updates at a glance.
Regularly review code to catch issues early on. Code reviews foster collaboration and improve overall package quality by leveraging different perspectives within the team.
Don’t forget about documentation! Keeping detailed records of changes made over time aids future troubleshooting efforts and keeps everyone on the same page regarding project evolution.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in SSIS-950
Troubleshooting in SSIS-950 can be a daunting task, but understanding common issues helps simplify the process. One frequent problem developers encounter is package execution failures. Often, these stem from incorrect configurations or missing components. Double-check connections and data sources to prevent unnecessary headaches.
Another issue arises with variable scopes. If variables aren’t set correctly within containers, unexpected behaviors can occur during runtime. Always verify that your variables exist at the intended scope level.
Performance bottlenecks are also a concern when working with SSIS-950 packages. Monitor data flow tasks for inefficiencies like blocking transformations and consider optimizing them by using asynchronous transforms where possible.
Error handling should never be overlooked. Implementing robust logging and notification systems will help identify problems early on, saving time in the long run as you navigate through development challenges.
Case Studies: Real-Life Examples of Successful Implementation
A leading retail company implemented SSIS-950 to streamline its data integration processes. By automating data flows from various sources, the organization reduced manual effort and improved accuracy. As a result, they achieved faster reporting times and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
Another example comes from a healthcare provider that faced challenges with patient data management. Utilizing SSIS-950 allowed them to integrate disparate systems effectively. The outcome was a centralized database that facilitated better patient care through timely access to vital information.
In the finance sector, a major bank adopted SSIS-950 for ETL tasks related to regulatory compliance. With robust error handling and logging features, they ensured data integrity during complex transformations, which significantly streamlined audit processes.
These case studies illustrate how diverse industries leverage the power of SSIS-950 to enhance operational efficiency and drive business success.
Conclusion and Future Outlook for SSIS-950
As the landscape of data integration continues to evolve, SSIS-950 stands out as a powerful tool for developers. Its capabilities offer robust solutions for managing complex workflows and ensuring data accuracy. The future appears bright, with ongoing advancements likely enhancing its functionality further.
With each iteration, we can expect improvements that cater directly to user needs. This evolution may lead to more streamlined processes and increased automation potential within ETL operations. Staying up-to-date with these changes is crucial for leveraging SSIS-950 effectively.
Embracing best practices now will set the foundation for tackling challenges down the line. As organizations increasingly rely on data-driven decisions, investing time in mastering SSIS-950 will prove beneficial. Developers who prioritize efficiency and optimization will undoubtedly gain a competitive edge in their projects.
The road ahead looks promising for those willing to adapt and innovate using SSIS-950’s full potential. Engaging with the community and sharing insights could pave new paths toward success in this dynamic field.
TECHNOLOGY
Sell Steam Gift Card in Nigeria Today – Get the Best Rates Instantly

If you’re holding a Steam gift card and wondering what to do with it in Nigeria, you’re not alone. Many people receive Steam gift cards as gifts or rewards but don’t play PC games or simply need the cash instead. The good news is, you can easily sell Steam gift card in Nigeria and get instant payment in naira if you choose the right platform.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the smartest ways to sell Steam gift cards in Nigeria, how to avoid scams, and how to get the best exchange rates instantly. We’ll also introduce you to a trusted platform MyRidima where selling Steam cards is fast, secure, and rewarding.
What Is a Steam Gift Card?
Steam gift cards are prepaid digital vouchers that can be used to purchase games, in-game content, software, or other items on the Steam platform. They come in different denominations like $20, $50, $100, and even higher values.
However, if you don’t use Steam regularly or at all these cards can feel like unused currency. That’s where the gift card exchange market in Nigeria comes in.
Why Sell Steam Gift Cards in Nigeria?
Here are the top reasons people choose to sell Steam gift card in Nigeria:
- Cash in Your Hands: Convert digital value into naira for real-world needs.
- Gift Conversion: Turn unwanted gifts into useful funds.
- Avoid Devaluation: Steam gift card values can drop depending on demand; sell while the rates are still high.
- Safe Trading Opportunities: Verified platforms now offer escrow systems, removing the risk of getting scammed.
How to Sell Steam Gift Card in Nigeria – Step-by-Step Guide
Selling a Steam gift card in Nigeria is easier than you might think, especially with reliable platforms like MyRidima.
Here’s a step-by-step process to follow:
Step 1: Go to a Trusted Platform
Start by visiting a verified and reputable platform like MyRidima. This platform allows you to sell gift cards securely with guaranteed payouts.
Step 2: Select Your Card Type and Country
Steam gift cards come from different regions (e.g., US, UK, EU), and their rates can vary. Select the card type and country of origin to get the most accurate rate.
Step 3: Use the Live Rate Calculator
MyRidima offers a real-time calculator that tells you how much naira you’ll receive before you commit. This helps you make an informed decision and maximize your return.
Step 4: Upload the Card Details
You’ll be asked to upload a clear image or input the code of the Steam gift card. Make sure the card is unused and clearly visible to avoid delays.
Step 5: Get Paid Instantly
Once the card is verified, your payment is processed immediately. With MyRidima, most users receive their funds within minutes, directly into their Nigerian bank account or preferred wallet.
Why Choose MyRidima?
With so many platforms out there, why should you use MyRidima to sell your Steam gift card in Nigeria?
Here’s what sets it apart:
Instant Payment
MyRidima processes payments as soon as your gift card is verified. No long waits, no excuses.
Best Exchange Rates
You’ll get some of the highest rates in Nigeria for your Steam gift cards especially for US and UK cards.
Secure Transactions
The platform uses a secure and encrypted system to protect your card details and personal information.
Easy-to-Use Interface
Whether you’re a first-timer or a frequent seller, the interface is simple, user-friendly, and fast.
24/7 Customer Support
Have questions? MyRidima’s support team is available round the clock to assist you.
Tips for Getting the Best Rate When Selling Steam Gift Cards
To make sure you walk away with the best deal, consider the following:
- Sell During High-Demand Periods: Holidays and global sales events often raise the resale value.
- US Region Cards Have Higher Value: US-based Steam cards tend to sell at higher rates than UK or EU cards.
- Keep Cards in Good Condition: Clear images and undamaged cards speed up the process and reduce price cuts.
- Use Platforms with Transparent Rate Calculators: This ensures you know exactly what you’ll earn before trading.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
While it’s easy to sell Steam gift cards in Nigeria, many people still fall into avoidable traps. Here’s what to watch out for:
- Dealing with Unverified Vendors: Telegram and WhatsApp traders can be risky.
- Ignoring Exchange Rates: Don’t settle for platforms that won’t show you live rates.
- Not Double-Checking the Card Code: Always verify your card before uploading to avoid delays.
- Falling for Too-Good-to-Be-True Offers: Unrealistic rates usually signal a scam.
Final Thoughts
Selling a Steam gift card in Nigeria no longer has to be a gamble. With reliable platforms like MyRidima, you can convert your digital gift into instant naira safely, quickly, and at competitive rates.
So whether you’ve got a $20 card or $200 worth, don’t let it go to waste. Sell your Steam gift card in Nigeria today and enjoy the ease of secure transactions and fast payments.
TECHNOLOGY
Easy steps to record your screen for free online by itop

For many professionals, recording their computer screen is an essential task for creating tutorials, presentations, or sharing information with colleagues. However, finding a reliable and user-friendly screen recording tool can be a challenge. That’s where itop comes in. This online platform offers an easy and free way to record your screen with just a few simple steps. In this blog post, we will walk you through the process of using itop to record your screen effortlessly and efficiently. Whether you’re a teacher, business professional, or content creator, itop can help you achieve your screen recording goals with ease.
Overview of iTop: A Free Online Screen Recording Solution
iTop is a versatile online platform that empowers professionals to effortlessly record their computer screens. iTop makes screen recorder easier for a variety of uses, such as making tutorials, presentations, and group projects, thanks to its intuitive interface and practical capabilities.This free tool is especially beneficial for teachers, business professionals, and content creators seeking a reliable solution to capture their screens effectively. Stay tuned as we delve into the key features and functionalities of iTop, guiding you on how to leverage this powerful tool for your screen recording needs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Recording Your Screen with iTop
Now that we have explored the capabilities of iTop for screen recording, let’s delve into a step-by-step guide on how to effectively utilize this tool. From accessing the platform to selecting recording settings and editing options, we will provide you with a comprehensive walkthrough to ensure a seamless recording experience. By following these easy steps, you can harness the full potential of iTop to create engaging and informative screen recordings for your professional or personal projects.Now let’s explore the usefulness of using iTop to easily record your computer screen.
Key Features of iTop for Effective Screen Recording
iTop offers a range of key features that make screen recording a breeze. One of the standout features is its user-friendly interface, allowing even beginners to navigate the tool with ease. Additionally, iTop provides customizable recording settings, enabling users to adjust parameters such as video quality and audio input according to their preferences. Moreover, the editing options in iTop allow for seamless post-production tasks, including trimming, adding annotations, and enhancing visuals. Stay tuned as we delve deeper into these key features of iTop to help you elevate your screen recording game.
Tips for Optimizing Your Screen Recording Experience
To enhance your screen recording experience using iTop, consider these tips. Make sure to prepare your script or outline beforehand to ensure a concise and clear recording. Adjust your recording settings in iTop to match your desired video quality and audio input levels. Utilize the editing features to enhance your content by adding annotations, trimming unnecessary parts, and incorporating visual effects. Furthermore, take breaks during longer recordings to maintain focus and energy. Stay tuned for our upcoming blog posts where we will share more expert tips on maximizing your screen recording potential with iTop.
Typical Problems and Solutions for iTop Users
Encountering technical glitches while using iTop for online screen recorder can be frustrating. Some common issues users face include audio synchronization problems, recording lag, and file compatibility issues. To address these challenges, ensure that your device and internet connection meet the minimum requirements for smooth operation. Try restarting the application or your device if you encounter any issues. Additionally, regularly update iTop to access the latest bug fixes and improvements. If problems persist, consider reaching out to iTop’s support team for personalized assistance. Stay proactive in troubleshooting to optimize your screen recording experience with iTop.
Conclusion: Enhancing Your Workflow with Free Screen Recording Tools
To sum up, using iTop to become proficient at screen recording can greatly improve the effectiveness of your workflow. By addressing common issues and implementing troubleshooting tips, you can harness the full potential of this free online tool. Remember to stay proactive in optimizing your recording experience by keeping your device updated and reaching out to iTop’s support team when needed. With a seamless screen recording process, you can create engaging tutorials, presentations, and demonstrations effortlessly. Embrace the power of technology and elevate your content creation with iTop’s user-friendly features. Start recording your screen today and unlock a world of possibilities for your digital projects.
TECHNOLOGY
Benefits of Data Science for Fraud Detection and Transaction Security in Fintech
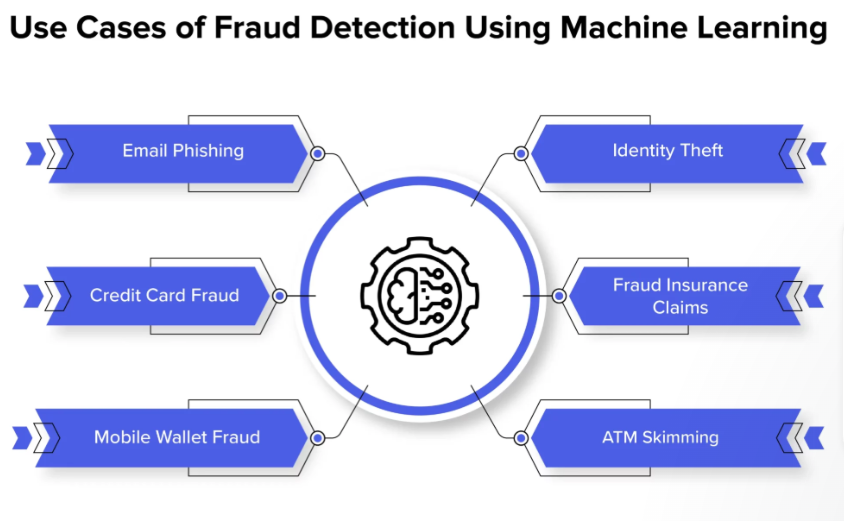
Introduction to Data Science in Fintech
Fintech continues to reshape how consumers and businesses access, transfer, and safeguard their money. Data science is at the heart of this transformation—a discipline that empowers financial institutions to extract valuable patterns from massive datasets. As many companies leverage data science to outpace online threats, the need for sophisticated technical expertise becomes increasingly apparent. In today’s world, where transaction speed and reliability are paramount, firms like David Johnson Cane Bay Partners help set the standard for using data-driven insights to improve financial protection. Firms based in the Cane Bay Virgin Islands specialize in fintech consulting and collaborate with other organizations to develop advanced analytical frameworks that address emerging security challenges.
Industry consultants deliver practical guidance beyond traditional risk management by turning unstructured transaction data into tangible intelligence. As global cybercrime rises, integrating machine learning models and analytics into financial operations gives fintech players a significant edge.
Transforming Fraud Detection with Advanced Analytics
One of the most significant impacts of data science in fintech is its ability to revolutionize fraud detection. Pattern recognition algorithms and predictive analytics analyze transaction histories, identifying questionable activities before they result in financial losses. With robust data science tools, fintech companies flag suspicious behaviors and accelerate investigations, minimizing potential damage. According to a report from the Statista Fintech Segment, integrating data science-driven fraud detection reduces costs and decreases the frequency of breaches.
Artificial intelligence extends these capabilities further, helping fintech platforms distinguish between legitimate and risky activities more accurately. Rapid identification of abnormal patterns enables institutions to proactively respond, protect customer assets, and sustain market confidence.
Enhancing Transaction Security with Real-Time Insights
With digital transactions occurring around the clock, real-time monitoring powered by data science is now essential. Machine learning models assess millions of data points per second, flagging inconsistencies in individual transactions and across systems. This immediate detection blocks cyberattacks before they escalate, offering protection for both users and financial infrastructure.
Companies that invest in continuous analytics benefit from rapid alerts and faster responses. By leveraging consulting expertise from experienced teams, fintech organizations tailor their algorithms to specific customer environments and compliance demands, leading to an adaptive framework that evolves as new threats emerge. This adaptability is crucial for maintaining trust in a highly competitive fintech landscape.
Consulting Expertise in Fintech Data Science
The value of data science is maximized with the guidance of consulting experts who understand both the technology and the financial regulatory landscape. Firms that focus on consulting bring objectivity and a breadth of experience across several verticals, enabling them to design solutions that integrate seamlessly with existing financial systems. A fintech consulting firm is a notable example, providing actionable insights, predictive risk models, and customized analytics to help fintech companies combat fraud and reinforce their transaction frameworks.
Consulting services extend beyond initial implementation. By offering ongoing monitoring, regular security updates, and incident response planning, these firms ensure fintech clients remain resilient against evolving cyber threats.
Regulatory Compliance and Customer Trust
Staying abreast of financial regulations is critical for safety and credibility in fintech. Data science provides transparency and traceability, making compliance reporting much more efficient. Detailed analytics support audit trails, while anomaly detection models demonstrate that an organization actively protects user interests. The European Union’s tightening standards around customer data have clarified the need for robust analytics.
With clear governance and the right consulting partnerships, fintech companies can boost client confidence, streamline their operations, and maintain a strong reputation within the digital economy.
Why the Cane Bay Virgin Islands Plays a Strategic Role
As an emerging hub for innovation, fintech consulting firms are strategically positioned to attract world-class consulting expertise and foster collaborations that further fintech advances. Talent-rich and connected to global financial networks, the region serves as a launching pad for progressive initiatives in transaction security and fraud prevention. Firms work closely with partners across industries to bring real-time solutions and long-term strategic advice to the fintech sector.
Future Outlook for Data Science in Fintech Security
The combination of analytics, automation, and expert consulting will be crucial for countering increasingly sophisticated cyber threats. As transaction volumes grow and regulatory expectations rise, fintech organizations must continue to innovate with advanced analytics and proactive risk management. Consulting partners play an essential role in empowering these companies with the resources needed to evolve and adapt. The future of data science in fintech security is promising, driven by ongoing investment in machine learning and a commitment to resilient, user-focused financial systems.
-

 TECHNOLOGY2 weeks ago
TECHNOLOGY2 weeks agoHow the Creators of Izonemedia360.com Are Redefining Digital
-

 Crypto2 weeks ago
Crypto2 weeks agoDiscover How Be1Crypto is Transforming Cryptocurrency Learning
-

 TECHNOLOGY2 weeks ago
TECHNOLOGY2 weeks agoUnlocking Success: Coyyn.com Digital Business
-

 TOPIC3 weeks ago
TOPIC3 weeks agoLwedninja: The Ultimate Resource for Aspiring Ninjas
-

 Crypto4 weeks ago
Crypto4 weeks agoA Comprehensive Review of ecrypto1.com Crypto Wallets
-

 Crypto2 weeks ago
Crypto2 weeks agoCrypto30x.com Gemini: Smarter, Safer Crypto Trading
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoget_ready_bell:client_pulse – The Intelligent Core of Client Retention
-

 Business5 months ago
Business5 months agoA Deep Dive into Pedrovazpaulo Human Resource Consulting
